Do your legs often feel numb, tingly, or colder than usual? Poor blood circulation could be the reason. When blood flow is restricted, your muscles and tissues don’t get enough oxygen and nutrients, leading to discomfort and other health concerns.
Circulation issues in the legs can develop over time or suddenly, affecting mobility and overall wellbeing. Ignoring the signs may lead to more serious complications. Before exploring solutions, let’s examine what causes poor circulation and how it affects the legs.
What Causes Poor Circulation in General?
Poor circulation happens when blood flow slows down or becomes blocked, preventing oxygen and nutrients from reaching tissues. The circulatory system relies on the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries to transport blood throughout the body. When this process weakens, certain areas, like the legs, receive less blood than they need.
Restricted blood flow causes symptoms such as cold feet, numbness, and swelling. If left untreated, it can lead to tissue damage, ulcers, infections, and blood clots.
Causes of Poor Leg Circulation
Several conditions and lifestyle factors reduce blood flow to the legs. Some affect the arteries, limiting blood flow to the lower limbs. Others weaken the veins, preventing blood from returning to the heart.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) and Atherosclerosis
PAD develops when fatty deposits accumulate in the arteries, reducing the space for blood to flow properly. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, reduces circulation and increases the risk of pain, cramping, and slow-healing wounds.
Without treatment, PAD can lead to serious complications, including tissue damage and ulcers. Plaque buildup in the arteries is also a major contributor to PAD and can increase the risk of heart disease.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Blood Clots
A blood clot in a deep vein can block circulation and cause swelling, redness, and discomfort. DVT often forms in the legs and becomes dangerous if the clot travels to the lungs. Prompt medical attention helps prevent life-threatening complications.
Diabetes and Blood Vessel Damage
High blood sugar weakens blood vessels and nerves, reducing circulation in the legs and feet. Many people with diabetes experience slow wound healing and an increased risk of infections. Poor circulation in diabetics can also lead to nerve pain, numbness, and foot ulcers.
Lack of Physical Activity
Sitting or standing for long periods slows circulation and increases the risk of swelling and discomfort. Muscles play a key role in helping blood return to the heart. Regular movement helps improve blood flow and prevents fluid buildup in the legs.
Obesity and Increased Pressure on Veins
Excess weight strains the veins, making it harder for blood to flow back to the heart. This increases the risk of circulation problems like varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency. Maintaining a healthy weight relieves pressure on blood vessels and supports better circulation.
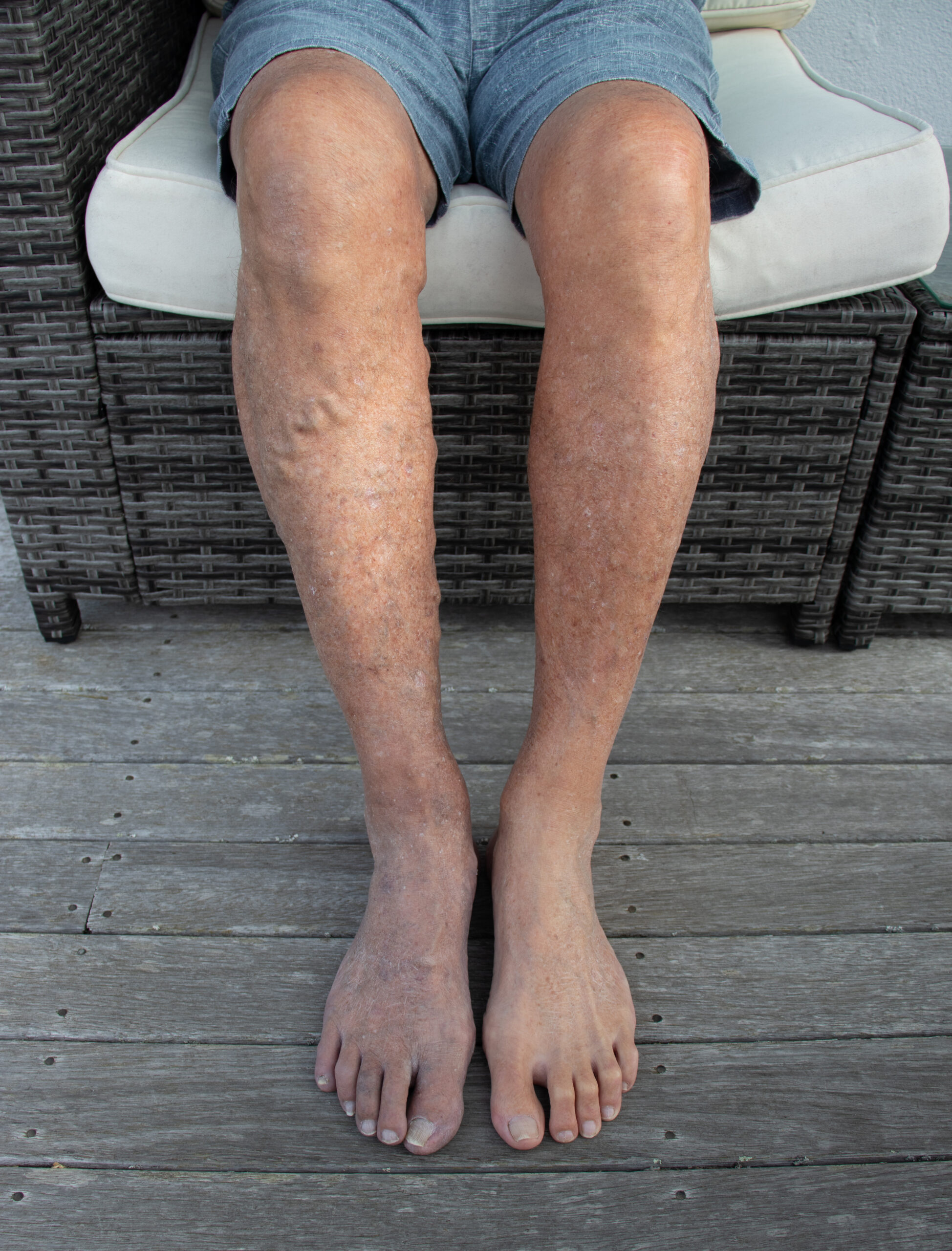
Varicose Veins and Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
Weakened vein valves allow blood to pool in the legs instead of flowing back to the heart. This leads to swelling, aching, and skin discoloration. Over time, vascular disease caused by poor circulation can result in ulcers and persistent leg pain.
High Blood Pressure and Circulatory Strain
Hypertension forces the arteries to work harder, reducing their flexibility and narrowing the passage for blood flow. Over time, this increases the risk of circulation problems and cardiovascular disease. Controlling blood pressure supports better circulation and overall vascular health.
Smoking and Blood Vessel Constriction
Nicotine causes blood vessels to tighten, reducing oxygen delivery to tissues. Smoking also damages artery walls and increases the risk of atherosclerosis. Quitting smoking helps blood vessels relax and improves circulation over time.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients, such as iron, vitamin B, and magnesium, weakens circulation. A poor diet can cause sluggish blood flow and increase the risk of vascular problems. Eating nutrient-rich foods supports healthy circulation and prevents deficiencies.
Cold Temperatures and Blood Flow Restriction
Exposure to cold weather causes blood vessels to constrict, reducing circulation to the extremities. This can make the legs and feet feel cold and numb, especially for individuals with existing circulation problems. Wearing warm clothing and staying active helps maintain healthy blood flow.
Symptoms of Circulation Issues in Legs
Poor circulation in the legs often starts with mild discomfort but can progress to more serious complications. Depending on the underlying cause, the symptoms may appear gradually or suddenly. Recognizing these warning signs early can help prevent long-term damage.
Cold Feet and Toes
Poor blood flow makes it harder for the body to regulate its temperature. The legs, feet, and toes may feel cold, even in warm environments. Persistent coldness can indicate an issue with the arteries or veins.
Numbness and Tingling
Reduced circulation limits oxygen delivery to nerves, causing a pins-and-needles sensation. This symptom may come and go or persist over time. Chronic numbness can signal a serious condition like PAD or nerve damage from diabetes.
Leg Pain and Cramping
Oxygen-deprived muscles may cramp or ache, especially during movement. People with PAD often feel pain when walking, which improves with rest. Muscle fatigue and heaviness in the legs can also occur after prolonged standing or sitting.
Swelling in Legs and Ankles
When blood pools in the veins, fluid leaks into surrounding tissues, causing swelling. This is common in people with venous insufficiency or heart-related circulation problems. The swelling may worsen after sitting or standing for long periods.
Skin Discoloration
Poor circulation affects how the skin receives oxygen and nutrients. Legs may appear pale, bluish, or reddish, depending on the condition. Persistent discoloration may indicate severe circulation problems that need medical attention.
Slow-Healing Wounds and Ulcers
Cuts and sores on the legs take longer to heal when circulation is impaired. In severe cases, ulcers may form, increasing the risk of infection. Diabetics and individuals with PAD are especially vulnerable to this complication.
Some symptoms may seem minor at first, but they can worsen without treatment.
What to Expect During a Circulation Diagnosis
If you have symptoms of poor circulation, your doctor will perform a series of tests to find the cause. The process includes a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and diagnostic tests to measure blood flow. These steps help determine whether the issue comes from narrowed arteries, weakened veins, or an underlying condition.
Discussion of Symptoms and Medical History
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, such as numbness, swelling, or leg pain. They will also review your medical history, including conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or a history of blood clots. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, diet, and activity levels are also considered as they affect circulation.
Physical Examination
A hands-on exam helps identify visible signs of poor circulation. Your doctor may check for swelling, skin discoloration, or slow-healing wounds. They might also feel your pulse in different areas of your legs to assess blood flow.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Test
This simple, noninvasive test compares blood pressure in your ankles and arms. A lower reading in the ankles may indicate narrowed arteries or peripheral artery disease. The test is painless and provides a quick assessment of how well blood is reaching your legs.
Doppler Ultrasound
A Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of blood flow in your veins and arteries. Your doctor may use this test to check for blockages, blood clots, or varicose veins. It’s a noninvasive procedure that helps detect circulation problems affecting the legs.
Angiography and Advanced Imaging
If a more detailed look at your blood vessels is needed, your doctor may order an angiography. This involves injecting a contrast dye into the bloodstream and using X-rays, CT (computed tomography) scans, or MRIs (magnetic resonance imaging) to find blockages. These tests provide a clearer picture of circulation problems.
Blood Tests for Underlying Conditions
Since diabetes, high cholesterol, and clotting disorders affect circulation, blood tests may be done to check for these risk factors. Identifying these conditions early can help manage circulation issues before they become more serious.
Once testing is complete, your doctor will explain the results and discuss treatment options.
How to Improve Circulation in Legs
Restoring healthy blood flow requires a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes. Some cases respond well to daily habits, while others need medical intervention. It depends on the cause and severity of the condition.
Medications to Improve Circulation
Doctors may prescribe medications to help blood move more easily. Blood thinners, such as aspirin or anticoagulants, reduce the risk of clots. Other medications, like vasodilators, help widen blood vessels to improve circulation.
Compression Therapy
Compression socks or stockings help prevent blood from pooling in the legs. They apply gentle pressure, supporting vein function and reducing swelling. Many people with varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency benefit from wearing them daily.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Doctors may recommend procedures to restore blood flow for severe blockages. Angioplasty uses a small balloon to open narrowed arteries, often followed by stent placement. Sclerotherapy and laser treatments help treat varicose veins by closing off damaged veins.
Surgical Treatments
In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary. Bypass surgery creates a new path for blood to flow around blocked arteries. Vein stripping or ablation removes damaged veins that cause circulation problems. These procedures are typically reserved for severe or nonresponsive cases.
Hydration and Proper Nutrition
Drinking enough water helps keep blood from thickening, making circulation smoother. Nutrients like iron, vitamin B, and omega-3 fatty acids support vascular health. Avoiding excessive salt and processed foods helps reduce swelling and blood pressure problems.
Quitting Smoking and Managing Blood Pressure
Smoking narrows blood vessels, restricting circulation. Quitting allows arteries to expand and improves oxygen delivery to tissues. Keeping blood pressure in a healthy range prevents long-term damage to arteries and veins.
Get Effective Treatment for Circulation Issues at Wellness and Pain
If you have leg pain, swelling, or numbness, you need real solutions, not temporary relief. At Wellness and Pain, we treat circulation issues with a combination of advanced medical care and practical lifestyle guidance.
Our specialists provide orthopedic care, trigger point injections, massage therapy, acupuncture, and IV hydration. Whether you need targeted pain relief or long-term circulation support, we find the right treatment based on your condition and daily challenges.
Poor circulation can also contribute to other health concerns, including chest pain and erectile dysfunction. Addressing circulation problems early can improve overall well-being and prevent more serious complications.
You don’t have to live with discomfort or wait for symptoms to get worse. If you’re dealing with circulation problems in your legs, schedule an appointment with Wellness and Pain to get the right treatment.
FAQs About Circulation Issues in Legs
How do you fix poor circulation in legs?
Improving circulation in the legs often requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Regular exercise, such as walking or stretching, helps blood flow more easily. Eating a heart-healthy diet, staying hydrated, and quitting smoking also support better circulation.
If needed, doctors may recommend compression therapy, medications, or minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty to restore blood flow.
What are signs of poor circulation in your legs?
Common symptoms include cold feet, numbness, tingling, or leg cramps, especially after walking. Swelling, skin discoloration, slow-healing wounds, and a heavy or aching sensation in the legs can also indicate circulation problems.
What is the best vitamin for blood circulation in legs?
Several vitamins help improve circulation, including vitamin B3 (niacin), which widens blood vessels, and vitamin C, which strengthens blood vessel walls. Vitamin E supports healthy blood flow by preventing clotting, while vitamin K helps regulate blood thickness. Omega-3 fatty acids and magnesium also promote better circulation by reducing inflammation and relaxing blood vessels.
At what age does poor circulation start?
Circulation problems can develop at any age, but the risk increases with age. People over 40 are more likely to experience poor circulation due to conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. However, younger individuals with a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, or smoking habits may also develop circulation issues.